Child abuse is a severe and widespread issue that affects children across all demographics and regions. It encompasses physical, emotional, and sexual abuse, as well as neglect. Here’s a deeper look at its facets and impacts:
Types of Child Abuse:
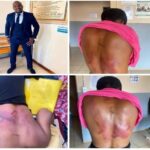
– Physical Abuse: Involves causing physical harm to a child through actions such as hitting, burning, or shaking.
– Emotional Abuse: Includes verbal abuse, constant criticism, and rejection, leading to psychological trauma.
– Sexual Abuse: Involves any sexual activity with a child, including molestation, rape, and exploitation.
– Neglect: The failure to provide basic needs such as food, shelter, medical care, and supervision.
Signs of Child Abuse:
– Physical Signs: Unexplained bruises, burns, or fractures.
– Behavioral Signs: Withdrawal, anxiety, depression, aggression, or fearfulness.
– Developmental Signs: Delays in physical, emotional, or intellectual development.
Effects on Children:
– Short-term: Injuries, fear, anxiety, and difficulty trusting others.
– Long-term: Chronic health issues, mental health disorders (such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety), difficulties in relationships, and a higher likelihood of substance abuse.
Prevention and Support:
– Education: Teaching children about their rights and how to seek help.
– Support Systems: Creating safe environments in schools and communities where children can report abuse.
– Counseling and Therapy: Providing mental health support to help children recover from abuse.
– Legal Measures: Strengthening laws and regulations to protect children and prosecute abusers.
Role of Society:
– Awareness: Educating the public about the signs and consequences of child abuse.
– Reporting: Encouraging people to report suspected abuse to authorities.
– support: Offering resources and support to at-risk families to prevent abuse.
Child abuse is a community issue that requires a collective effort to address. By being vigilant and supportive, society can help protect vulnerable children and offer them a chance for a better future.



0 Comments